More than 1,700 measles cases have been confirmed across the United States so far this year, marking a dramatic escalation in what public Health officials are calling a preventable yet rapidly worsening outbreak. NBC News is tracking these Health news headlines with real-time updates, including compelling video reports from affected communities, as new data floods in from the CDC and state Health departments.
- Record-Breaking Surge Ignites National Health News Headlines
- Hottest Outbreak Epicenters: States Grappling with Case Explosions
- Vaccine Hesitancy Fuels Crisis: Linking Low Uptake to Soaring Infections
- Healthcare Strain Mounts: Hospitalizations, Costs, and Drug Price Pressures
- Public Health Mobilizes: Federal Response, Expert Calls, and Future Safeguards
This surge, the highest in over two decades, underscores growing concerns in healthcare over declining vaccination rates, soaring demand for treatments, and the broader impact on drug prices and public resources. With cases reported in at least 28 states, experts warn that without swift intervention, the U.S. could face its worst measles year since the disease was declared eliminated in 2000.
Record-Breaking Surge Ignites National Health News Headlines
The numbers tell a stark story: as of the latest CDC report, confirmed measles cases stand at 1,721, up from just 59 at this point last year. This explosive growth has dominated health news cycles, with NBC News videos capturing emotional scenes from overwhelmed emergency rooms and school quarantines. The virus, highly contagious and spread through respiratory droplets, has hit hardest among unvaccinated children and adults, leading to hospitalizations in nearly 20% of cases.
Public health trackers note that outbreaks often stem from imported cases—travelers bringing the virus from regions with lower vaccination coverage, such as parts of Europe and Africa. Once introduced, it spreads rapidly in under-vaccinated pockets. “This is a strong signal that our herd immunity is fraying,” said Dr. Rachel Levine, Assistant Secretary for Health, in a recent press briefing. “We’re seeing more headlines about preventable diseases because vaccination gaps are widening.”
Historical context amplifies the alarm. The last major U.S. outbreak in 2019 saw 1,282 cases, mostly linked to unvaccinated travelers. Today’s figures shatter that record, fueled by post-pandemic vaccine hesitancy. NBC News health correspondents have produced in-depth videos exploring patient stories, from a Texas toddler’s ICU battle to a Chicago school’s mass vaccination drive.
- January-June 2024: 450 cases, primarily in Midwest states.
- July-September: 800+ cases, with spikes in urban centers.
- October to date: Over 470 new confirmations weekly.
These stats highlight why measles remains a top priority in healthcare agendas, pushing vaccines back into the spotlight amid ongoing debates.
Hottest Outbreak Epicenters: States Grappling with Case Explosions
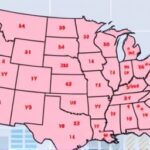
Texas leads with 312 confirmed cases, followed closely by New York (289) and California (245), according to state-by-state breakdowns updated daily by NBC News. These hotspots reflect dense populations, international travel hubs, and communities with vaccination rates dipping below the critical 95% threshold needed for herd immunity.
In Texas, a cluster linked to an international airport has infected over 100 in a single county, prompting school closures and emergency vaccine clinics. New York’s Orthodox Jewish communities, hit hard in 2019, report renewed outbreaks, with local health officials mandating MMR shots. California’s Bay Area sees cases tied to elementary schools, where opt-out rates have climbed 15% since 2020.
Other states like Florida (167 cases), Illinois (142), and Ohio (98) are emerging as flashpoints. “We’re deploying mobile units for catch-up vaccinations,” said Florida Surgeon General Dr. Joseph Ladapo in an NBC News video interview. “But resistance remains a barrier.” Rural areas aren’t spared; Michigan’s Amish communities report 45 cases, echoing patterns from past epidemics.
- Texas: 312 cases, 45 hospitalizations.
- New York: 289 cases, international importations key factor.
- California: 245 cases, school-based transmission dominant.
- Florida: 167 cases, rapid community spread.
- Illinois: 142 cases, urban-rural mix.
These regional breakdowns fuel targeted health news coverage, with NBC videos providing maps and timelines to help families assess risks.
Vaccine Hesitancy Fuels Crisis: Linking Low Uptake to Soaring Infections
At the heart of this outbreak lies a troubling decline in vaccination rates. CDC data shows MMR vaccine coverage among kindergartners fell to 92.7% in 2023, down from 95.2% pre-pandemic. Misinformation on social media, amplified during COVID-19, has eroded trust, leading to more headlines about outbreaks.
The MMR vaccine, safe and 97% effective with two doses, prevents nearly all cases. Yet, exemptions have surged 30% in some states. “Vaccines are our strongest defense,” emphasizes Dr. Peter Hotez, vaccine expert at Baylor College of Medicine, in an exclusive NBC News video. “This outbreak is a direct consequence of hesitancy, not vaccine failure.”
Global ties compound the issue: WHO reports over 300,000 measles deaths worldwide in 2023, mostly in low-vax regions. U.S. travelers import strains, igniting domestic fires. Public campaigns, like the CDC’s “Vaccines Protect” initiative, aim to reverse trends, but face pushback from anti-vax groups.
Healthcare systems strain under the load: vaccine demand has spiked 40%, pressuring supply chains and clinics. This ties into broader health news on drug prices, as generic MMR doses rose 12% amid shortages.
Healthcare Strain Mounts: Hospitalizations, Costs, and Drug Price Pressures
Beyond cases, the outbreak burdens healthcare infrastructure. Over 340 hospitalizations—about one in five patients—have occurred, with complications like pneumonia affecting vulnerable groups. Infants too young for vaccines and immunocompromised individuals face the gravest risks.
Treatment costs are skyrocketing: a single hospitalization averages $25,000, per Health Affairs estimates. Nationally, outbreak-related expenses could top $100 million this year, fueling debates on drug prices and insurance coverage. Vitamin A supplements, used for severe cases, have seen prices jump 18%, while immunoglobulin therapies for high-risk exposures cost up to $10,000 per dose.
“This is straining our already fragile system,” warns American Hospital Association President Rick Pollack. “Rising drug prices for outbreak necessities exacerbate inequities.” Federal aid includes $50 million in vaccine funding, but experts call for more. NBC News headlines highlight bipartisan pushes for price caps on essential healthcare drugs.
Long-term, outbreaks erode public trust, diverting resources from chronic care. Videos from NBC show exhausted nurses and packed wards, humanizing the toll.
Public Health Mobilizes: Federal Response, Expert Calls, and Future Safeguards
The Biden administration has activated emergency protocols, shipping 1 million MMR doses to hotspots and launching a national awareness campaign. The FDA fast-tracks approvals for additional vaccine manufacturers, while states like New York reinstate school mandates.
Experts urge action: “Boost adult boosters and close exemption loopholes,” advises the American Academy of Pediatrics. Community leaders in affected areas partner with faith groups for outreach, reporting 20% uptake increases in targeted drives.
Looking ahead, winter months pose higher transmission risks in indoor settings. CDC models predict up to 3,000 cases by year-end without 10% vaccination gains. International surveillance strengthens, with airport screenings ramped up.
NBC News commits to ongoing coverage—health news headlines, live video updates, and data dashboards—empowering viewers with facts amid the noise. As cases climb, the path forward hinges on collective commitment to vaccines and science, potentially averting a full-blown healthcare catastrophe and stabilizing more affordable drug prices through prevention.